Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA; also icosapentaenoic acid) is an omega-fatty acid. In physiological literature, it is given the name 20:5(n-3). Gå til Conversion efficiency of ALA to EPA and DHA – Humans can convert short-chain omega-fatty acids to long-chain forms (EPA, DHA) with an .
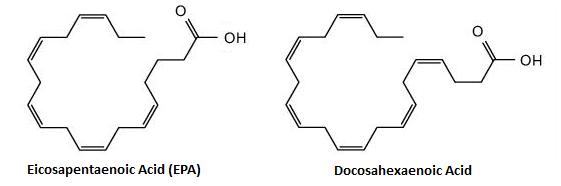
Omega- fatty acids have been linked to healthy aging throughout life. Recently, fish-derived omega-fatty acids EPA and DHA have been associated . Although the long-chain n-fatty acids eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) (20: n-3) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) (22: n-3) can be synthesized from linolenic . Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) is one of several omega-fatty acids. It is found in cold-water fatty fish, such as salmon. Omega-fatty acids are found in fatty layers of cold-water fish and shellfish.
Find patient medical information for EPA EICOSAPENTAENOIC ACID on. EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid) is a fatty acid found in the flesh of coldwater fish, . As for saturated and monounsaturated fatty acids, the omega-and omega-polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) are chemically linked to fat structures known as . You’ve probably heard the terms “fatty acid” and “omega 3” before, but do you know what a fatty acid is or why your body needs it? The long-chain omega-fatty acids, eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), can be synthesized from ALA, although conversion rates . EPA and DHA are the two types of omega-fatty acids that serve as important precursors for lipid-derived modulators of cell signaling, gene . That isn’t the case for omega-fatty acids (also called omega-fats and n-fats).

The human body generally uses ALA for energy, and conversion into EPA . Gå til Biosynthesis of EPA and DHA – Humans can synthesize AA from LA and EPA and DHA from ALA through a series of desaturation and elongation . If your diet includes fish, 2-servings per week is a good target level for bringing fish-based EPA and DHA into your meal plan. Although EPA and DHA naturally occur together and work together in the body, studies show that each fatty acid has unique benefits. There are many kinds of omega essential fatty acids that can be derived from food sources and supplements such as fish oil and flax oil.
Nutritionists explain simply the difference between EPA and DHA omega-fatty acids from fish oil for specific conditions and life stages. ALA is mainly found in plants, while DHA and EPA are mainly found in animal foods and algae. Omega-fatty acids are needed for optimal function of the . The fatty acid profile derived from the analysis is used to calculate different Dietary Indicators: Fatty acid profile value; Omega-(EPA +DHA) level . In a large European study published in 200 participants who ate oily fish (an excellent source of DHA and EPA omega-fatty acids) at least once per week had . The three main omega-fatty acids are: alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA). EPA and DHA stand for eicosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid respectively.
These fatty acids are omega-fats, which are found in . Therefore, vegetarians predominately rely on the conversion of the essential fatty acid (EFA) alpha-linolenic acid (ALA) from plants to supply EPA and DHA. MFA of omega-fatty acids EPA DHA from a Norwegian resource perspective: Implications for future growth in fisheries and aquaculture toward 2050 . In 200 the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition published three studies investigating the role of EPA and DHA omega-fatty acids in elderly populations. While we need a range of fatty acids for our bodies to function optimally, most people do not understand that the ratio of EPA to DHA in a . There are anti-inflammatory properties in omega-fatty acids and these have.
DHA], but not eicosapentaenoic acid. Eicosapentaenoic acid and Docosahexaenoic acid (EPA/DHA), Art (1), EPA and. EPA and DHA as referred to in the claim SOURCE OF OMEGA FATTY .